Understanding Group Management in Linux
Group management in Linux is a fundamental aspect of
system administration, enabling you to efficientlycontrol accesstofiles and resourcesbased onuser roles and permissions. Groups allow you to categorize users with similar privileges, streamlining permission management compared to individual user accounts.
Types of Groups
Primary Group
Secondary Group
Primary Group
Every user in Linux belongs to exactly
one primary group. This group is assigned automatically when theuser is createdand determines the default permissions for files the user creates.
Secondary Group
A user can be a member of zero or more secondary groups, granting them additional permissions associated with those groups.
System Files
/etc/passwd: This file stores user account information, including the username, encrypted password, UID, GID, primary group name, home directory, and login shell. The line for a newly created user will show their username, followed by anx(password is hidden), UID, GID, primary group name, home directory, and login shell (e.g.,/bin/bash).username:password:UID:GID:comment:home:shellFor More Info:-
https://cloudcoder.hashnode.dev/local-user-management#heading-passwd-and-shadows
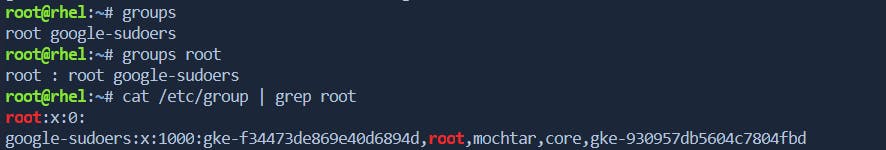
/etc/group: This file contains information about groups, including the group name, encrypted password (often left blank), GID, and a comma-separated list of users belonging to the group. The newly created group will have an entry in this file with the same name as the user, their GID, and the user listed as the only member.groupname:password:GID:group memberFor More Info:-
Group Management Commands
groups
The
groupscommand displays the groups to which a user belongs.
$ groups username
id
The
idcommand displays the user and group IDs associated with a user account.
$ id username

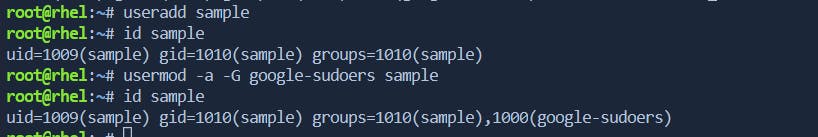
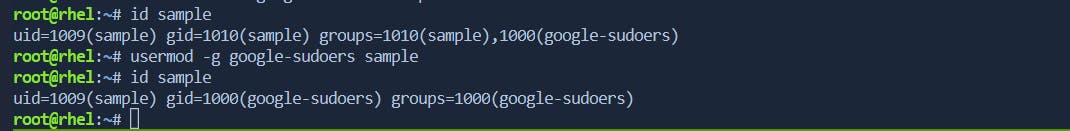
usermod
The
usermodcommand is used to modify user account properties, including group membership.
-a: Append the user to the supplementary group(s) listed without removing current group membership.
-G: Specify supplementary groups for the user.
-g: Set the primary group for the user.$ sudo usermod -a -G groupname username
$ sudo usermod -g newprimarygroup username
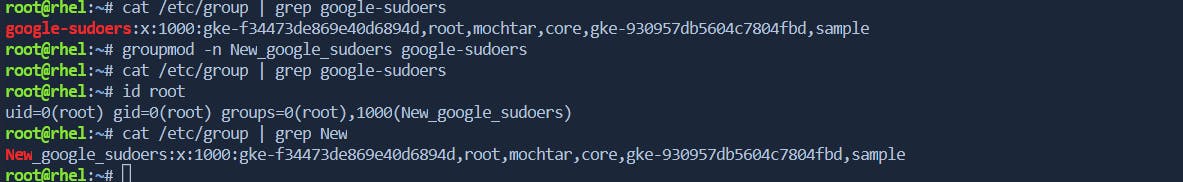
groupmod
The
groupmodcommand is used to modify group properties, such as the group name.$ sudo groupmod -n newgroupname oldgroupname
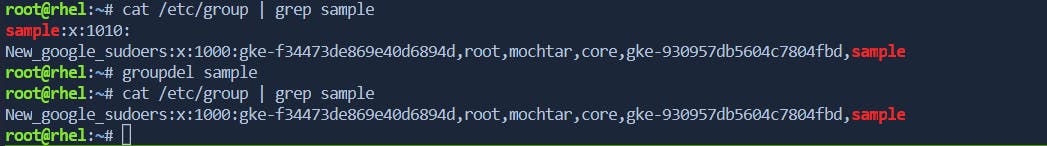
groupdel
The
groupdelcommand is used to delete a group from the system.$ sudo groupdel groupname
gpasswd
The
gpasswdcommand is used to administer the/etc/groupfile and manage group passwords.
-A: Set the group administrator.
-a: Add a user to the specified group.
-d: Remove a user from the specified group.$ sudo gpasswd -A admin groupname $ sudo gpasswd -a username groupname $ sudo gpasswd -d username groupnameNote:-
remove all Admins in a group
$ sudo gpasswd -A " " groupname
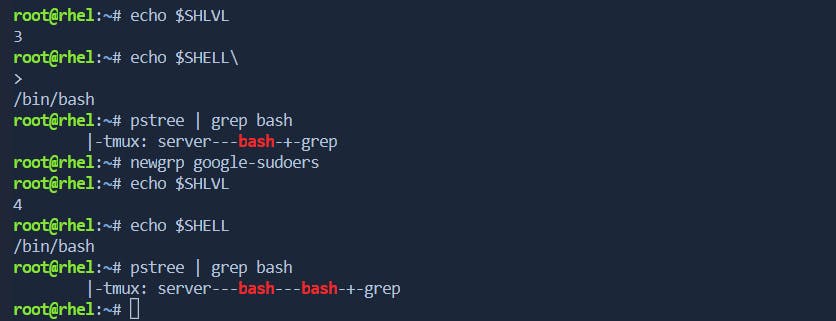
newgrp
The
newgrpcommand is used to change the current group ID, effectively switching to a new group.$ newgrp groupname